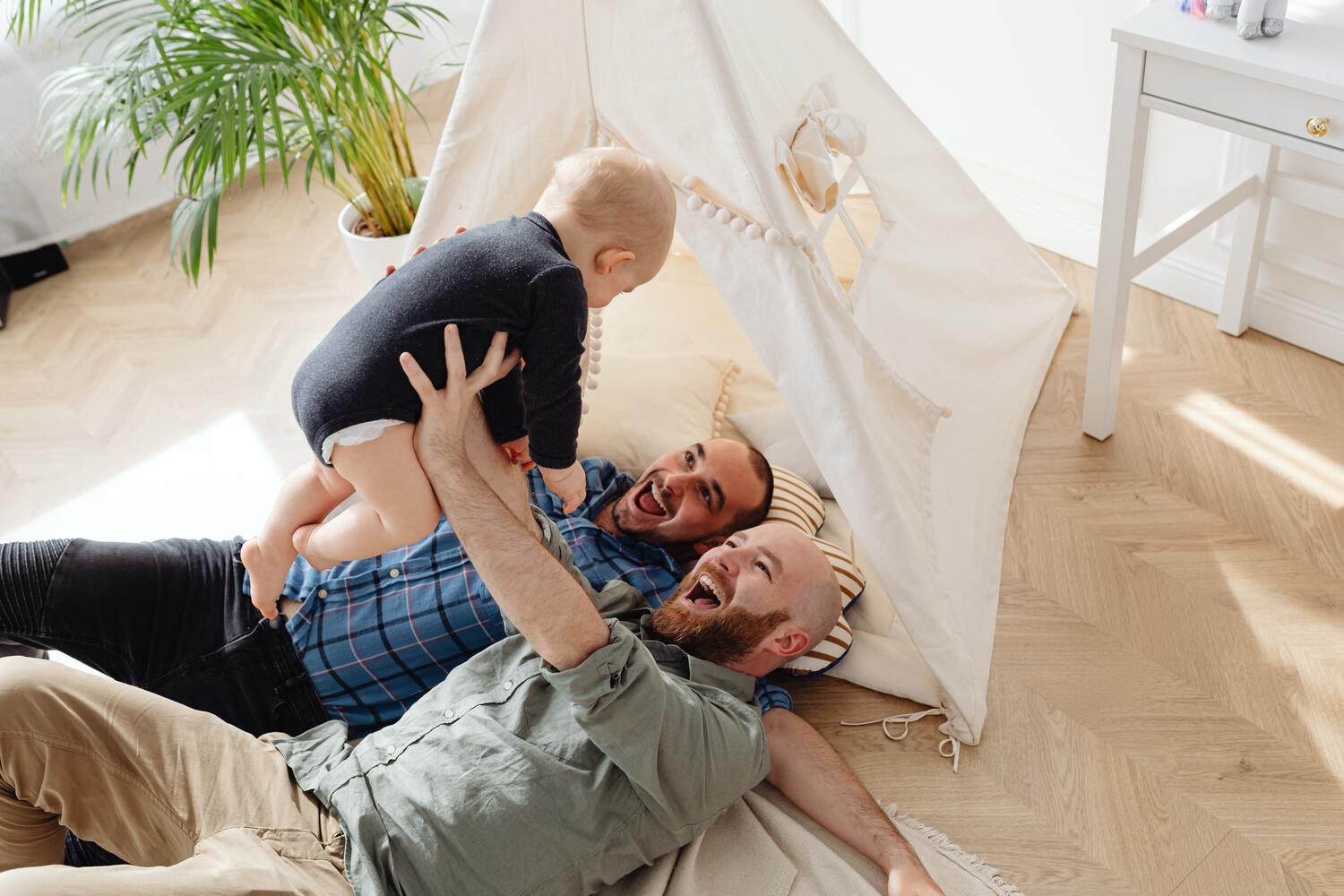

According to the National Survey of Family Growth conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 1 in 8 couples struggle with infertility––an estimated 49 million couples worldwide.
Building a family is a milestone for many people. Yet up until the 1960s, many individuals and couples across the world struggled to conceive and start a family.
Now, modern-day fertility treatments have made families a reality for couples struggling with infertility, with thousands of global organizations helping parents conceive. Thanks to much scientific advancement in the 21st century, we now have modern-day In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) to support individuals on their path toward parenthood.
IVF is an advanced form of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) that helps infertile women and couples conceive. Through IVF, eggs are manually fertilized using a sperm sample from a woman’s partner or donor.
There are many ways to tailor the In Vitro Fertilization process to intended parents, from reciprocal IVF for lesbian couples, to mini IVF treatments for people searching for a lower-impact, less expensive approach to fertility.
IVF has helped many couples with fertility issues successfully conceive, and may be right for you if you have or experience:
Additionally, those who are in a same-sex relationships or are intended single parents can achieve their dream of building a family through IVF.
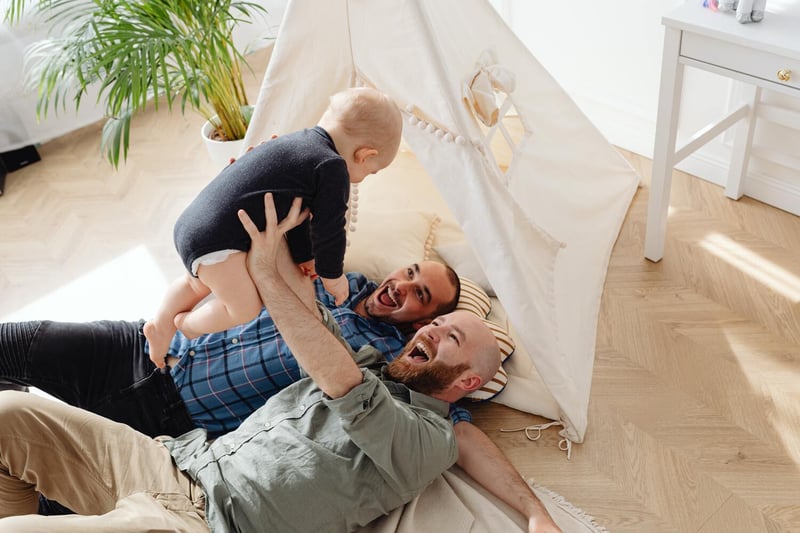

Since the introduction of IVF into mainstream medicine in the 1980s, nearly 5 million babies have been born through assisted reproductive technology (ART).
However, it’s also important to understand that IVF does not ensure a successful pregnancy. Some patients require multiple IVF cycles to achieve a successful pregnancy, while others unfortunately never achieve pregnancy at all.
Good candidates for IVF include:
IVF might not be as effective for:
Because IVF is unique to each patient’s situation, there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to fertilization. However, medications, blood tests, vaginal ultrasounds, sperm and egg retrieval, fertilization and embryo transfer are all critical elements of the process.
The IVF treatment process can be complex and daunting as a patient. It is important that you be as informed as possible throughout the entire process.
The IVF process has many elements:
When the IVF cycle begins, your clinic will order a number of pre-treatment tests. Some tests are mandated by state and federal law, while testing required by your clinician is customized to you. These tests often include a baseline ultrasound, bloodwork, and a semen analysis for the male partner to assess your fertility challenges and possibilities. However, other tests may also be required.
Ovarian stimulation is a critical part of egg production. By using fertility medications, women can prepare for egg retrieval and increase their chances of a successful pregnancy. Oral and injectable fertility medications are often recommended in addition to hormones for optimal results. This may be conducted with a transvaginal ultrasound to determine when the eggs have matured.
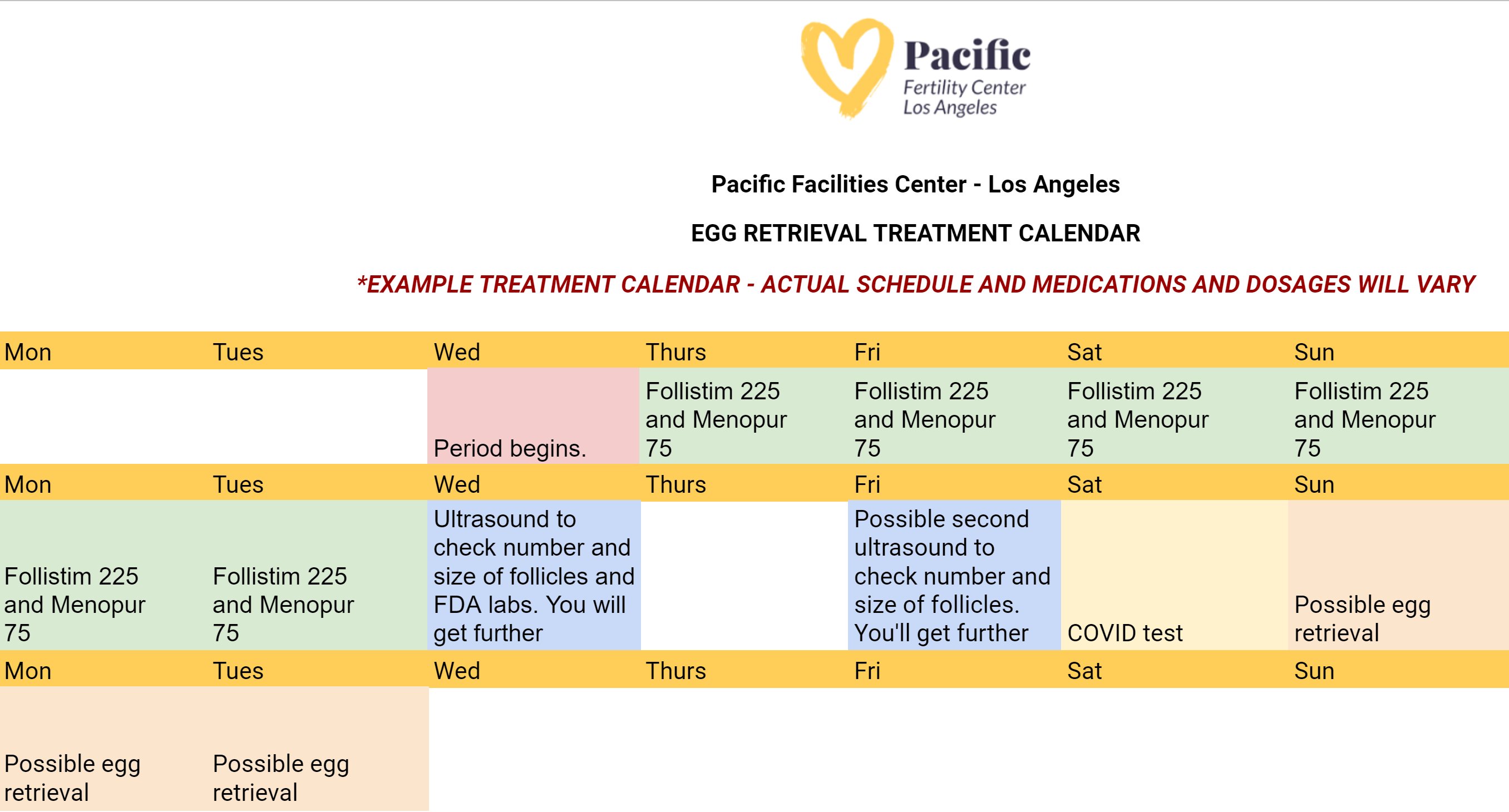
During the egg retrieval process, patients will receive general anesthesia to sleep during the procedure. Next, the eggs are then retrieved by placing a needle through the vaginal wall and into the ovary––and suctioned from the growing follicles and collected into test tubes. Finally, the test tubes are passed to the waiting embryologist. Here's what the egg retrieval calendar might look like:
Once the eggs are in the laboratory, they will be visualized under a microscope and prepared for fertilization with either fresh or frozen sperm. A process called ICSI or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection is then performed to inject one healthy sperm into each of the viable eggs.
The following morning, the embryologist will be able to determine how many embryos have formed. The embryos will typically spend 5-7 days in the laboratory before they are ready to be frozen, or transferred back to the uterus. Frozen embryos tend to have better success rates. Most patients will choose to test embryos for genetic or chromosome abnormalities prior to embryo transfer through preimplantation genetic screening or preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
Preparing for your embryo transfer is one of the most important processes in your IVF journey. Patients at PFCLA may receive an IVF embryo transfer calendar that resembles the following:
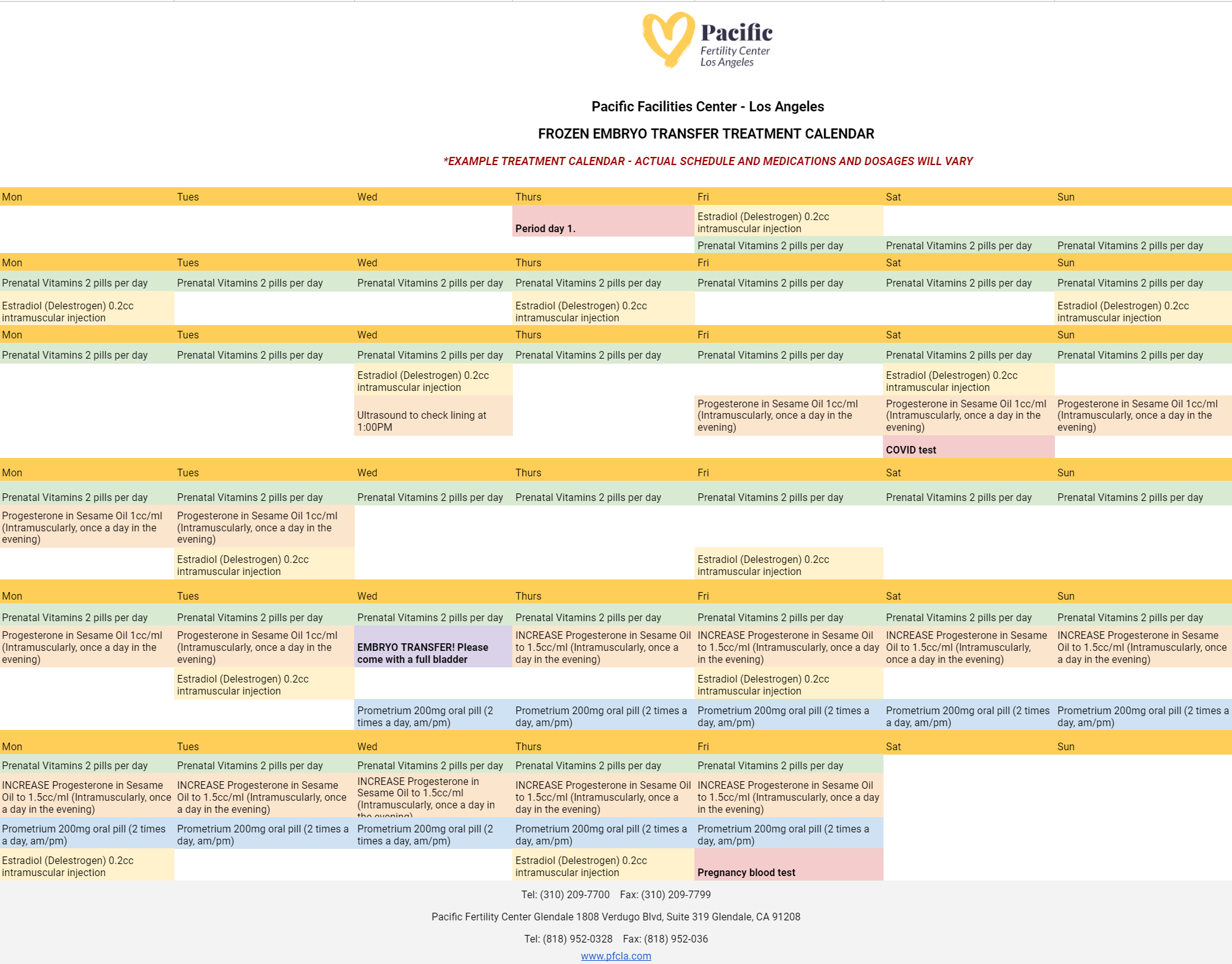
On the day of embryo transfer, the embryos will be graded based on their cell growth and development. This grading system, along with the patient’s age, will help the physician and patient to decide on the appropriate number of embryos to transfer.
An embryo transfer procedure feels similar to a pap smear and is performed while the patient is awake. To start, the cervix is visualized and cleaned. Then, a very thin catheter (tube) loaded with the embryo(s) is placed gently through the cervix and into the uterine cavity. The embryo(s) are placed near the top of the uterus using ultrasound guidance.
Approximately ten days after the transfer, a blood pregnancy test (hCG level) is performed to determine if the patient is pregnant.
There are multiple available fertility treatments available today, but some are less effective than others. It’s important to talk to your doctor about what will deliver the best chances of pregnancy, so you’re not wasting precious time and money on options that may not be right for you. IUI, or intrauterine insemination, is one of these treatment options that some use because it is minimally invasive, but the success rates are usually far lower than that of IVF.
After experiencing failed IUIs, many patients turn to IVF as a more reliable fertility treatment. IVF, or in vitro fertilization, oversees most of the stages of conception to increase the chance of a successful pregnancy. Although IUI is a viable and successful fertility treatment option, it is not uncommon for a patient’s first IUI attempt to fail.
But for most who are experiencing infertility, IUI is an inferior option to IVF because IUI acts only as an assistant to natural conception. For many patients seeking fertility treatment, it can be impossible to achieve pregnancy through IUI, and your doctor may recommend starting with IVF.
To prepare for IVF, intended parents will likely need various screenings--semen analysis, uterine exams, ovarian reserve testing, and even a mock embryo transfer. This is critical to your individual IVF success, and everyone’s process will look slightly different. Preparing for IVF requires consideration of your diet, blood testing, exercise, stress, and overall health.
Before undergoing IVF, your blood work will be used to assess the level of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in your system. This will give the fertility specialist an understanding of the quality and number of eggs you may have. Also, the blood work performed can help note possible incompatibilities between a mother’s blood type and father’s blood type. This blood work is also crucial in determining the presence of potential genetic disorders, viruses, and diseases that could affect the mother or baby’s health if pregnancy is achieved.
Without critical data from ultrasounds and blood work during the IVF process, the chances of a successful pregnancy are much lower, and fertility specialists can’t use the most modern techniques to truly aid patients in their journey to having a child. Additional testing may be part of the IVF process, depending on the challenges you’ve faced in getting pregnant.
After the embryo transfer, a blood test will be used to measure the pregnancy hormone levels of human chorionic gonadotropin in a woman’s system. The presence of this hormone confirms pregnancy and is typically tested for 11-12 days after an embryo transfer has been performed.
During IVF, it’s common for fertility doctors to prescribe various fertility medications to their female patients as part of the treatment process.

These fertility drugs are meant to trigger the release of various hormones and to regulate ovulation. By doing this, women are in essence made more fertile during the procedure, which improves the chances of pregnancy.
There are common fertility drugs that may be prescribed:
The exact medications and types of drugs required for your treatment will be determined during the consultation process. Keep in mind that some of these medications can be taken orally while others will be administered through injections.
Whatever drugs a patient requires, the effectiveness of these medications will require precise timing. Patients should take their fertility drugs as directed by their fertility specialist.
All fertility visits must also be attended on schedule to ensure optimal results. The improper dosage or administration of a fertility drug can result in a failed IVF cycle or reduced potential for a successful pregnancy.
When a woman is undergoing IVF treatment, the required fertility drugs can increase specific hormone levels, such as progesterone, to prepare the body for pregnancy. Just as when progesterone levels rise naturally during pregnancy, a patient’s increased progesterone levels during IVF are likely to cause fatigue.
While changes in hormone levels are the most prominent cause of fatigue during IVF, the condition can be further exacerbated by stress or anxiety.
By the time a woman undergoes IVF treatment, she has often been dealing with infertility issues for at least a year. The worry and anticipation of repeated failed pregnancy attempts can take both a physical and mental toll, so it is understandable that many patients already feel worn down when their IVF journey begins.
Make sure to talk through all your concerns with your fertility specialist to get peace of mind during treatments and receive resources for further emotional support if needed. This will ensure you feel prepared and comfortable during your IVF treatments. Some helpful resources could be therapy for trauma-related to previous pregnancies, talking to couples who have successfully undergone IVF or joining a support group for couples going through the same process.
Because IVF requires a variety of medications throughout the treatment process, patients undergoing IVF may experience a mixture of different side effects. However, the chances of starting a family through IVF far outweigh the possible side effects.
If you do experience one of these side effects, know that they are common and can be minimized to prevent discomfort. These side effects include:
However, more severe risks and complications associated with IVF can include:
These complications can bring side effects that should not be ignored. If you're experiencing the following, reach out to your doctor immediately:
Your fertility doctor should address the side effects of IVF, as well as offer tips to deal with these symptoms. When experiencing fatigue, cramping and other side effects, it’s recommended you:
Although mild cramping and pelvic discomfort are common, more severe pain should not be ignored. If your side effects are
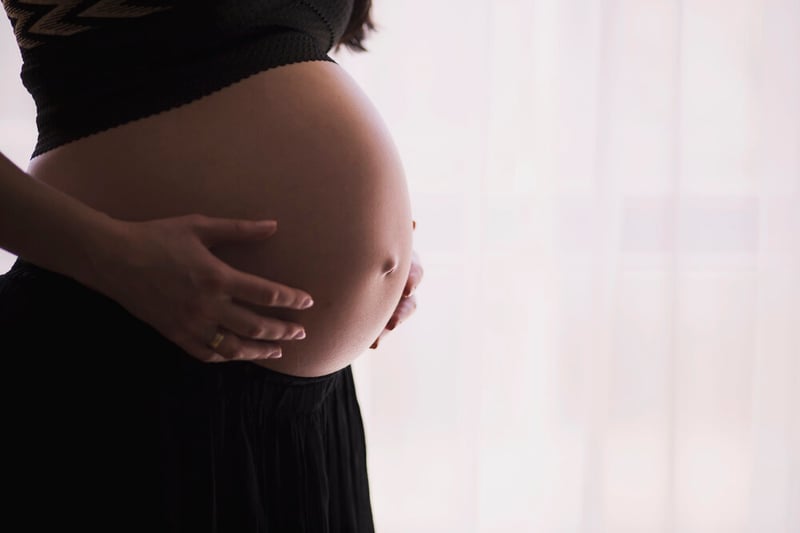

Success rates matter when it comes to the field of IVF, especially with surrogacy. Using the most experienced clinics with great success rates can provide you a better chance of having a successful pregnancy and birth, resulting in a healthy baby (or babies). You can ask any doctor or clinic for their success rates and protocols.
By having a conversation with your doctor about what you can expect, you’ll know what will and won’t be possible throughout your fertility journey. When it comes down to how many embryos will be implanted and what’s safe for you or your surrogate, trust your doctor’s counsel and let him guide you on the right path.
Out of nearly 118,000 cycle starts from intended egg retrievals including all embryo transfers record by SART performed in the United States in 2020, under 29% (SART) resulted in live births. By contrast, PFCLA has an over 44% (SART) live birth rate from cycle start per intended egg retrieval including all embryo transfers.
Bear in mind that comparing clinics to one another is rarely an ‘apples to apples’ comparison, as different clinics and the physicians therein take different profiles of patients based on age, risk factors and services offered (whether an egg donor was used etc…). The best thing you can do to understand your personal IVF profile is consult with a physician.
Building a family has never been more accessible and successful than ever. If you’re coping with infertility blues or looking to start your family but don’t know how, you don’t have to wait any longer to take steps toward this dream.
The fertility specialists at Pacific Fertility Center would be happy to answer any further questions you may have regarding your surrogacy options. Contact us to get started today.
These Stories on In-Vitro Fertilization
Fertility Services
Why PFCLA
Resources
Subscribe to our newsletter
Note: This is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Information provided is for general educational purposes only and is subject to change without notice. Speak to your doctor directly with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Any information contained herein does not replace any care plan as determined by a physician.
¹Birth rate percentage using aggregate data from ALL age groups on the Live Births Per Intended Egg Retrieval (ALL EMBRYO TRANSFERS) of Patient's Own Eggs chart for 2020. Reference: PFCLA SART | NATIONAL SART
© 2024 PFCLA. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy.
No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think